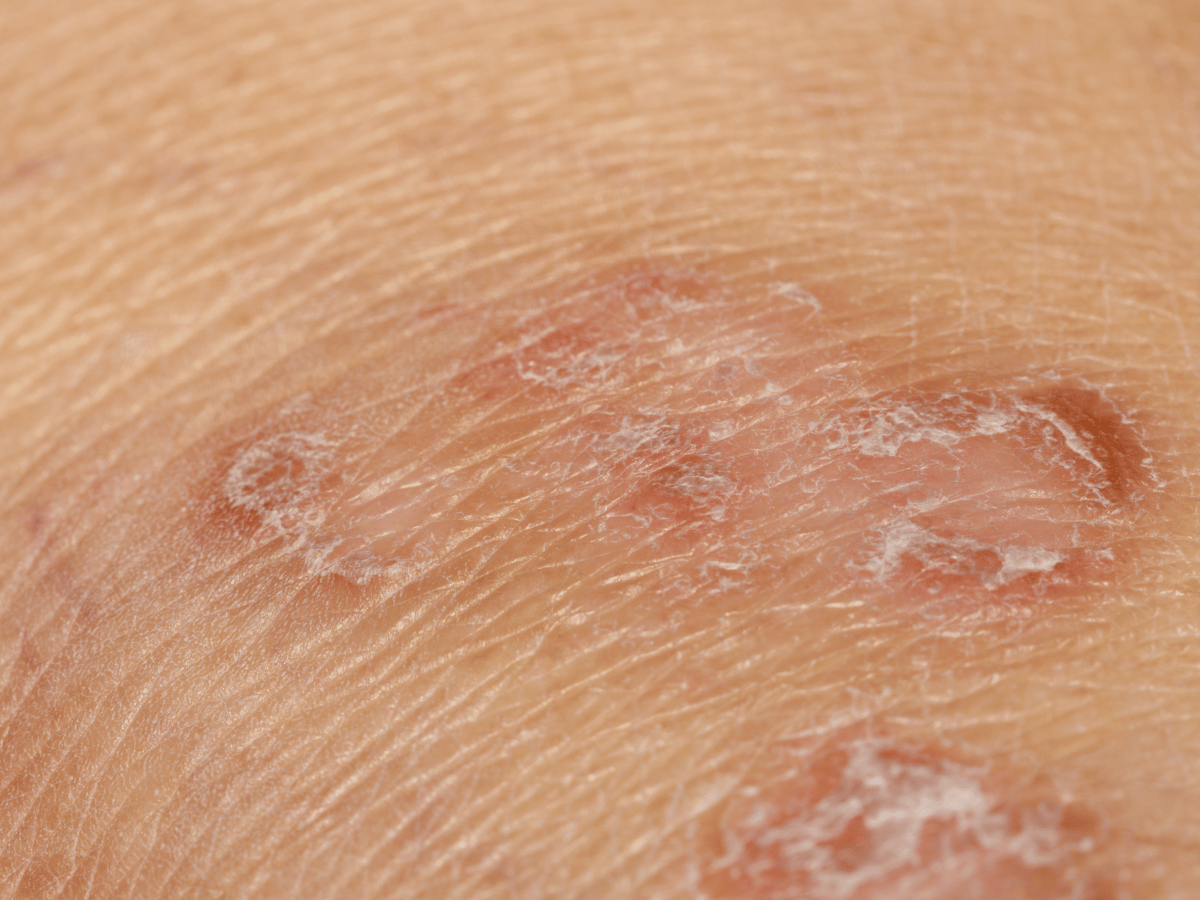
What Is Actinic Keratosis?
Actinic Keratosis (AK) is a precancerous lesion of the outer layer of the skin (the epidermis) and is caused by long-term exposure to sunlight. These sun spots appear to be scaly or crusty bumps on the surface of the skin. AKs are discolored and sometimes tender to the touch. Common locations for AKs are the face, ears, scalp, back of the neck, upper chest, hands, and forearms.
CAUSES
They usually form in sun exposed areas such as the face, scalp, and hands.
RISK FACTORS
Individuals who are fair skinned, have blue eyes or red or blond hair, or are outdoors much of the time are particularly susceptible to SCC development. Patients who are organ transplant patients have a significantly higher risk of developing AKs which transform into skin cancer.
SYMPTOMS
AKs are scaly sandpaper like lesions which can be painful or itchy. Often, our patients note that AKs “come and go in the same location”, are easily palpable, and have some type of discomfort, whether it be itching, tingling or burning.
FAQs
Why are actinic keratosis worrisome?
AKs may develop into squamous cell cancer (SCC) and have been associated with basal cell cancer (BCC) lesions. AKs may develop as early as the third and fourth decade of life. Untreated lesions have up to 20 % risk of progression to squamous cell carcinoma. Individuals who are fair skinned, have blue eyes or red or blond hair, or are outdoors much of the time are particularly susceptible to SCC development. Patients who are organ transplant patients have a significantly higher risk of developing AKs which transform into skin cancer.
What do actinic keratosis look like?
AKs are scaly sandpaper like lesions which can be painful or itchy. They can be categorized into four types of lesions:
- Hypertrophic subtype
- Pigmented subtype
- Atrophic subtype
- Lichenoid subtype
Often, our patients note that AKs “come and go in the same location”, are easily palpable, and have some type of discomfort, whether it be itching, tingling or burning.
Where do actinic keratosis form and where on the skin are they most dangerous?
AKs can form anywhere on the body. They usually form in sun exposed areas such as the face, scalp, and hands. They are most dangerous when they form over the lip or ear regions, as these areas are more susceptible to invasive cancer formation. If you notice recurrent AKs forming on your skin after they have been treated, you should follow-up with us for a re-evaluation and possibly a skin biopsy.
Visit Academic Alliance in Dermatology
Our team provides thoughtful, expert care for all your skin health needs. We are proud to offer the most advanced general, surgical and cosmetic dermatological services throughout Florida’s West Coast. Your best skin awaits.